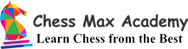The Queen’s Gambit Accepted (QGA) is a fundamental and respected opening in chess, where Black accepts the gambit pawn offered by White in the Queen’s Gambit.
It arises after the following moves:
1.d4 d5
2.c4 dxc4
Key Ideas for White
- Regaining the Pawn: White aims to recover the pawn on c4 quickly, usually by developing pieces and applying pressure on the c4 square.
- Moves like Nf3, e3, Bxc4 are common.
- Center Control: White often tries to establish a strong pawn center with moves like e4 after recovering the pawn.
- Typical moves: e3, Nf3, Bxc4, O-O, followed by e4.
- Piece Activity: White seeks active piece play, rapid development, and the creation of threats.
- Typical moves: Nf3, Bxc4, O-O, and sometimes Qa4+ to force Black’s pieces into less favorable positions.
Key Ideas for Black
- Solid Pawn Structure: Black aims to maintain a solid pawn structure, often planning to support the d5 pawn and create counterplay.
- Typical moves: Nf6, e6, c5.
- Piece Development: Black focuses on rapid development and controlling key squares, often playing for …e6 and …c5 to challenge White’s center.
- Typical moves: Nf6, e6, c5, Be7, O-O.
- Flexibility: Black maintains flexibility in pawn structure and piece placement, waiting for the right moment to strike in the center or on the queenside.
- Plans like …a6 to prepare …b5 are common.
In this game, GM Dlugy is playing black. The game started with 1.d4 d5 2.c4 dxc4 3.Nf3 a6 4.e3 e6 5.Bxc4, white recaptured the c-pawn and black developed his knight to f6.

The game continued 6.0-0-0 b5, attacking the bishop.
- White’s bishop retreated to d3 and GM Dlugy pushed the c-pawn to challenge the center.
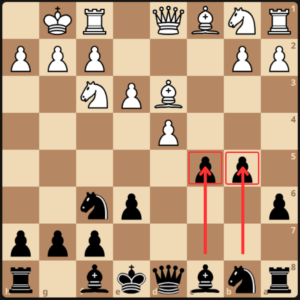
White replied 8.b3, defending the c4 square. 8…Bg7 9.Ba3, white attacks the c5 pawn, and GM Dlugy answers with Nbd7.
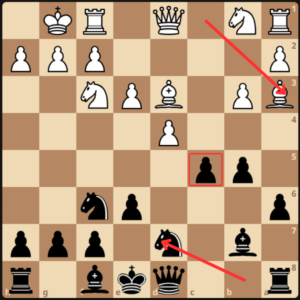
White brought out his other knight and developed to d2 and both rooks positioned to control the c-file. 10…Rc8 11.Rc1
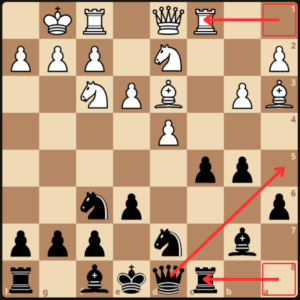
GM Dlugy moved his queen to a4, hitting the bishop. White decided to trade his bishop and pawn. 12.Bxc5 Bxc5 13.dxc5 Nxc5.
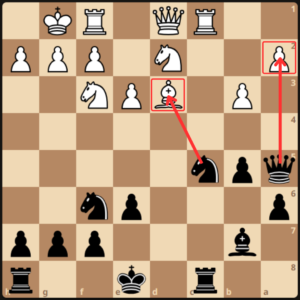
The opponent retreated his bishop to b1 to defend the a1 pawn and GM Dlugy castled kingside. White then developed his queen to e2 and black finished his development with h6.
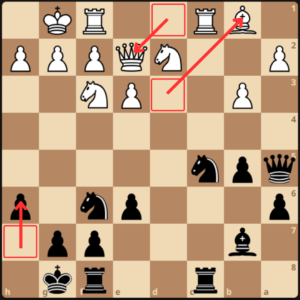
White’s knight jumped to e5, and GM Dlugy is eyeing an exchange in the e4 square via Nce4 – Nxe4, Nxe4 Bxe4 Bxe4, controlling the center with his bishop.
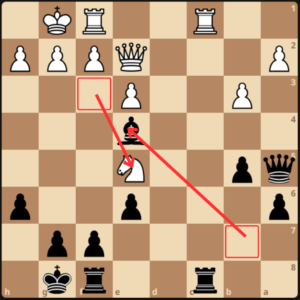
White jumped his knight to d7 hitting the rook, and GM Dlugy moved it to d8. Then a rook trade happened 20.Rxc8 Rxc8.
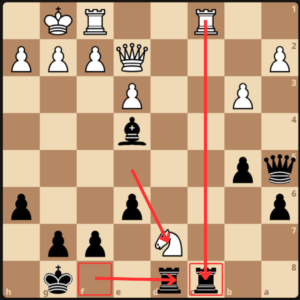
White brought out his queen to g4, attacking the bishop and creating some tactical ideas. Black easily defended with Bf5, baiting Nf6.
Black’s idea is to pressure the a2 pawn with Rc2, trying to win the pawn.
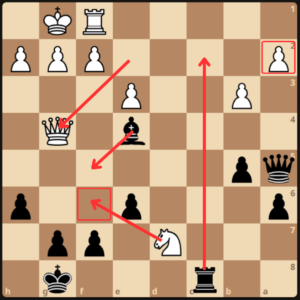
White played Qd4 and GM Dlugy grabbed the free pawn on a2. The opponent replied with an ambitious g4, attacking the bishop but also opening his kingside position.
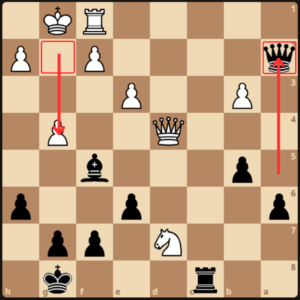
Black simply retreated the bishop on g6. 24.b4 Rc4, a strong move to pick another pawn.
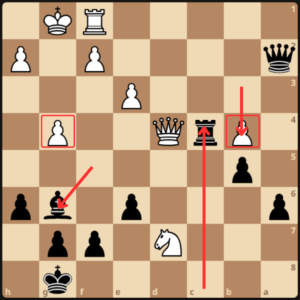
White put his queen back to d1 and black picked up the b-pawn, now up 2 pawns, and planning to play Rb1 next to trade and simplify. White answered with a tricky move Nf8 (if Kxf8 then Qd8#) but GM Dlugy did not fall for it and played Qd5 stopping any chance of counterplay.
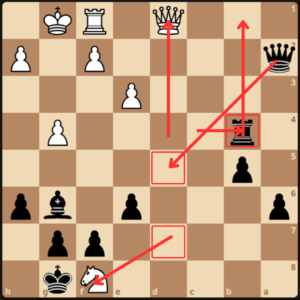
White then proceeded 27.Nxg6 and GM Dlugy answered with the queen trade 27…Qxd1 28. Rxd1.
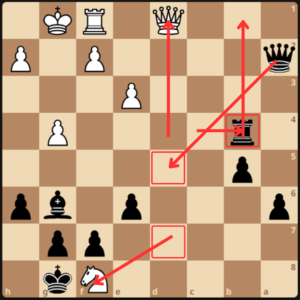
At this point, white is losing as black’s next moves are Rxg4+ Rxg6, up a total of 3 pawns with 2 connected passers on the a and b files. White resigned.


Summary